India Quality Control: The Essential Blueprint for Global Importers

Sourcing products from India presents a world of opportunity: cost-effective manufacturing, skilled craftsmanship and immense production capacity. However, these advantages can quickly turn into significant losses without a definitive and well-executed quality control (QC) strategy.
For global importers, the phrase "India quality control" represents the critical barrier between a successful product launch and a costly recall. It’s the system that ensures your vision is perfectly translated into a manufactured product, batch after batch.
This guide moves beyond basic definitions to provide a strategic, timeless framework for implementing robust quality control in India. Whether you're a seasoned importer or new to sourcing from South Asia, this blueprint will help you protect your brand, ensure customer satisfaction and safeguard your bottom line.
What is the Manufacturing Landscape in India?
Effective QC is not a one-size-fits-all process; it must be tailored to its environment. India's manufacturing ecosystem is uniquely characterized by its diversity, which is both its greatest strength and its biggest QC challenge.
- Diversity of Scale: The landscape ranges from large, automated facilities serving global brands to smaller, specialized workshops adept at artisan crafts and textiles. Your QC approach must be scaled accordingly.
- Cluster-Based Production: India specializes in geographic hubs for specific goods—Tiruppur for knitwear, Morbi for ceramics, Jalandhar for sports goods. Understanding these clusters helps you anticipate common region-specific defects.
- Cultural Context: Building a strong, respectful relationship with your supplier is paramount. Clear, documented communication is essential to ensure that agreements and specifications are understood and adhered to, preventing misunderstandings down the line.
Read more about the manufacturing landscape in India and what brands should consider
What is the Three-Pillar Approach to Quality Control?
Relying solely on a final pre-shipment inspection is a high-risk strategy. True quality is built into the process through a multi-layered approach that identifies issues at the most cost-effective stage.
1. Initial Production Check: Laying the Foundation
Initial Production Check (IPC) is the most crucial stage for defect prevention. Before mass production begins, you must ensure absolute clarity.
- Raw Material Verification: Do not assume incoming materials are correct. Verify the quality of fabrics, components, metals and polymers against agreed-upon standards before they enter the production line.
- Tech Pack Agreement: Conduct a detailed review of your technical pack with the factory manager. Ensure every material specification, measurement tolerance, stitch type and color code is unequivocally understood.
- First Article Inspection (FAI): Once the first sample is produced, inspect it with extreme rigor. This sample sets the benchmark for all future production and validates the factory’s capability.
2. During Production Inspection (DUPRO): The Early Warning System
A During Production Inspection is conducted when 15-30% of the order is complete. This is your chance to catch process-related errors before they become endemic.
- The Power of DUPRO: It identifies issues like machine miscalibration, operator error or consistent assembly mistakes early. Correcting these issues mid-stream prevents an entire order from being defective, saving immense time and cost on rework.
- Focus: Check production methods, semi-finished products and assembly line quality controls.
3. Final Random Inspection (FRI): The Final Verification
Final Random Inspection (FRI) is the most common inspection, performed on 100% finished, packaged goods. This final audit determines if the goods meet the agreed standards and are ready for shipment. This is where the AQL standard is applied.
Discover the Top Quality Control Inspection Companies in India
The AQL Standard: The Engine of Objective QC
The Acceptable Quality Limit (AQL) is the universal language of quality inspection. It is an objective, statistical methodology (based on ISO 2859-1) that determines the scope of an inspection and the acceptability of a production lot. It removes emotion and subjectivity from the decision-making process.
How AQL Works in Practice:
For a large order, checking every single item is impractical. AQL uses statistical sampling to provide a representative assessment.
- Sample Size: Based on the order quantity, an AQL chart determines how many units to pull randomly from the total lot.
- Acceptance/Rejection Criteria: The chart defines the maximum number of allowable defects.
- Critical Defects (AQL 0.0): Defects that pose a safety risk (e.g., sharp edges, electrical faults). Zero are acceptable.
- Major Defects (AQL 2.5): Defects that affect functionality, performance or saleability (e.g., broken zipper, major scratch). The tolerance for these is very low.
- Minor Defects (AQL 4.0): Defects that do not significantly impact usability (e.g., minor stitching issue, slight color deviation). A small number may be acceptable.
Key Insight: The AQL level you specify (e.g., Major 1.5, Minor 4.0) clearly communicates your quality expectations to the supplier. This must be agreed upon in writing before production commences.
AQL vs 100% Inspection: Which Quality Control Method is Right for You?
Critical Checklists for Key Indian Product Categories
The inspection checklist is your tool for applying the AQL standard. Focus areas vary significantly by product type.
For Apparel and Textiles:
- Workmanship & Stitching: Seam integrity, stitch density, loose threads.
- Dimensions & Measurements: Ensuring all pieces are within tolerance.
- Fabric Quality: Checking for defects like holes, runs or shading variations.
- Accessories & Trims: Functionality and placement of zippers, buttons, snaps.
- Labeling & Packaging: Accuracy of care labels, size tags and poly bags.
For Hardware, Machinery and Metals:
- Dimensions & Tolerances: Precise verification using calipers, gauges and CMMs.
- Material and Finish: Checking for correct material grade, plating quality, painting defects or rust.
- Functionality & Assembly: Ensuring parts fit together and operate as intended.
- Safety Compliance: Verifying products meet relevant international safety standards.
For Handicrafts and Artisan Products:
- Artistic Consistency: Managing expectations for natural variations in hand-made products.
- Material Authenticity: Confirming the use of promised materials (e.g., solid wood, authentic clay).
- Structural Durability: Checking the strength of joints, finishes and overall construction.
- Color and Design Fidelity: Ensuring the final product matches the approved prototype.
What are the Common Pitfalls in Indian Quality Control and How to Avoid Them?
Most QC failures are not due to a single error but a series of missteps.
- Supplier Selection Based on Price Alone: The cheapest supplier often cuts corners on quality.
Solution: Conduct thorough supplier audits. Assess their infrastructure, internal QC processes and client references.
Also Read: How to Find a Supplier in India?
- Unclear or Verbal Specifications: Assumptions lead to defects.
Solution: Invest in a detailed, visual tech pack. Document every requirement and ensure it is signed off by the supplier.
- The "Hands-Off" Approach: Absence from the process until shipment.
Solution: Implement the multi-stage QC process. Maintain consistent communication and require regular production updates.
- Lack of On-the-Ground Expertise: Absence of third-party inspection agencies
Solution: Partner with a reputable third-party inspection company. Their local, product-specific inspectors provide an unbiased assessment and understand regional nuances, offering invaluable peace of mind.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
1. Why are third-party inspections important in India?
India’s diverse supplier base and varying factory standards make inspections crucial.
2. What types of inspections are offered?
Initial Production, DUPRO, Final Random, Container Loading, 100% Inspection.
3. What products need inspection?
Apparel, footwear, electronics, furniture, toys, homeware etc.
4. How long does an inspection take?
Typically 1 working day depending on the quantity and complexity of the product.
5. Is the inspector familiar with Indian standards?
Yes! Trained in global + local (ISO/BIS) standards.
6. Can I get a real-time inspection report?
Yes! Digital reports with photos same day.

Building a Foundation of Trust and Quality through Testcoo
Mastering quality control in India is not a single event, it’s a disciplined, proactive strategy. By combining multi-stage inspections, AQL-based evaluation, supplier audits and compliance-focused processes, importers not only protect their shipments but also align with secure and trustworthy supply chains.
At Testcoo, we bring years of global QC expertise to help brands sourcing from India strengthen supplier relationships, reduce risks and ensure compliance with both customer expectations and international trade requirements.
From initial production checks to final inspections, Testcoo’s local teams provide reliable, data-driven insights empowering importers to build resilient supply chains, safeguard their reputation and grow with confidence.
Free Sample Report Performance Quality Control
Download a sample report to keep control of your supply chain!
Featured Articles
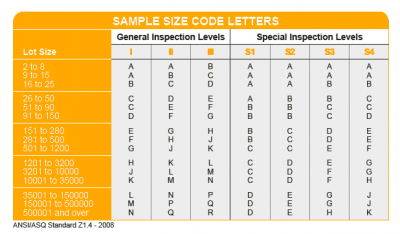 AQL Table | How to Read It
AQL Table | How to Read It TOP 10 Common Defects in Garments Quality Inspection
TOP 10 Common Defects in Garments Quality Inspection Product Packaging and Shipment Label requirements for Amazon FBA
Product Packaging and Shipment Label requirements for Amazon FBA What Is ASTM-F2413-18? Protective Footwear Standard
What Is ASTM-F2413-18? Protective Footwear Standard How to Conduct Third-Party Quality Control Inspections for Electric Scooters
How to Conduct Third-Party Quality Control Inspections for Electric Scooters SMETA Audit-What is SMETA Audit?
SMETA Audit-What is SMETA Audit? TESTCOO Supplier Verification/Certification Service SLCP, Higg FEM, GRS, GOTS
TESTCOO Supplier Verification/Certification Service SLCP, Higg FEM, GRS, GOTS Quality Control Inspection Company in China
Quality Control Inspection Company in China What is Quality Inspection? A Complete Guide
What is Quality Inspection? A Complete Guide Guidelines for Product Inspection in India
Guidelines for Product Inspection in India
Category
- Production Inspection Service
- Factory Audit
- Softline Inspection
- Hardline Inspection
- Electrics Inspection
- Certification
- Checklist
- Manufacturers
- Quality Assurance Basics
- Products Recall
- AQL
- Guidence and Standard
- News
- Supplier Management
- Amazon
- Protective Equipment
- e-commerce quality control
- Indian Manufacturing
- Soft Goods Quality Control
- Supply Chain Management
- Supply Chain Resilience
- E-Commerce Quality Control
- ISO 2859
- Supply Chain Optimization
- Garment Industry
- Higg Index




