Understanding AQL in Product Inspections: A Complete Guide to Quality Control

↵
In today's global supply chain, ensuring product quality is critical for brands, retailers and manufacturers. One of the most widely used quality control standards in product inspections is the Acceptable Quality Limit (AQL). AQL sets the maximum number of defective units considered acceptable in a given sample size during an inspection. Understanding AQL is essential for businesses to maintain consistent quality and reduce risks associated with poor-quality products.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what AQL is, how it is applied in product inspections, why it is crucial for businesses and best practices to implement an effective AQL-based quality control process.
What is Acceptable Quality Limit (AQL)?
AQL is a statistical measure used in quality control that determines the highest number of defective units allowed within a specific sample size before a batch is rejected. It is part of the ISO 2859-1 standard, which provides guidelines for sampling plans in inspections.
AQL helps businesses balance quality assurance and cost efficiency. It prevents the need for 100% inspection, which can be time-consuming and expensive while ensuring an acceptable level of quality in production.
History and Evolution of AQL
The concept of AQL was developed as part of military standards during World War II to ensure the reliability of manufactured goods. Over time, it became an industry-wide standard, evolving into ISO 2859-1, which is now used globally across various industries, including textiles, electronics, automotive and consumer goods.
How AQL Works in Product Inspections
Product inspections are conducted using a random sampling method based on AQL standards. The process follows these key steps:
- Determine the Lot Size: The total number of units in a production batch.
- Choose an Inspection Level: The inspection level dictates the sample size and is categorized into three general and four special levels. Higher inspection levels result in a larger sample size.
- Identify AQL Levels: Businesses set AQL limits for different defect categories: Critical, Major and Minor Defects.
- Use the AQL Table (ANSI/ASQ Z1.4 or ISO 2859-1): The table helps determine the sample size and acceptable defect limits based on the lot size and chosen AQL levels.
- Inspect and Classify Defects: Inspectors examine the selected sample and classify defects accordingly.
- Decision Making: If the number of defects in the sample exceeds the acceptable limit, the batch fails the inspection.
Types of Inspection Levels in AQL
AQL sampling plans offer different levels of inspection based on quality requirements:
- General Inspection Levels I, II, III: Used for most standard product inspections.
- Special Inspection Levels S-1, S-2, S-3, S-4: Used for highly specific, targeted tests (e.g., destructive testing).
Most companies choose Level II as the default standard unless a stricter level is required.
How to Read an AQL Table
There are two main tables. The first table “Sample size code letters” helps to determine the appropriate 'code letter.' The second table “Single Sampling Plans for Normal Inspection” shows the sample size and the maximum allowable number of defects based on the ‘code letter’.
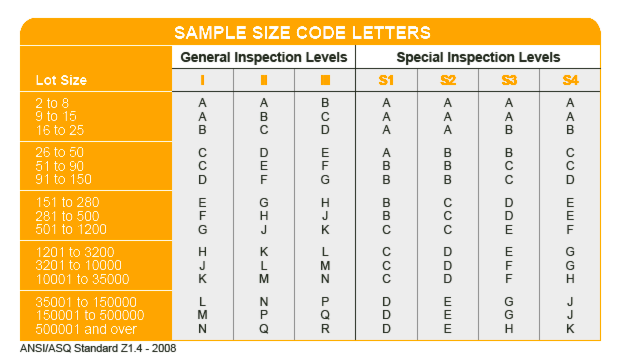
How to Read Sample size code letters Table?
Let's assume your lot size falls between 3,201 pcs and 10,000 pcs, and your inspection level is II. Based on this, the corresponding code letter is “L”.
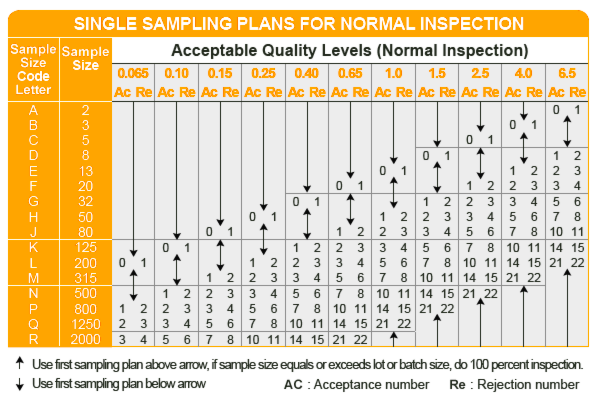
How to read Single Sampling Plans for Normal Inspection table?
Our code letter is “L”, which means you need to randomly select 200 pieces from the total lot size.
Assuming your AQL is set at 2.5% for major defects and 4.0% for minor defects, here are the acceptance limits:
- The lot is accepted if there are no more than 10 major defects and no more than 14 minor defects.
- The lot is rejected if these limits are exceeded.
For example:
- If you find 15 major defects and 12 minor defects, the lot is rejected.
- If you find 3 major defects and 7 minor defects, the lot is accepted.
AQL Defect Categories
AQL classifies defects into three main categories based on their impact on functionality, safety and appearance:
- Critical Defects (0% AQL): These defects make a product unsafe or unusable. Even a single critical defect results in a failed inspection.
- Major Defects (Typically 2.5% AQL): These defects affect the product’s functionality or durability, making it unsellable to end customers.
- Minor Defects (Typically 4.0% AQL): These are small imperfections that do not significantly affect product performance but may reduce customer satisfaction.
Examples of Defects in Different Industries
- Apparel: Loose threads (minor), misaligned stitching (major), chemical contamination (critical).
- Electronics: Scratches on casing (minor), malfunctioning button (major), battery leakage (critical).
- Toys: Minor paint imperfections (minor), loose parts (major), toxic material usage (critical).
Read more: Product Defects | How can you identify them?
AQL Sampling Plans and Standards
AQL sampling plans follow the ANSI/ASQ Z1.4 (ISO 2859-1) standard, which outlines the acceptable sample sizes and defect limits based on AQL levels.
For example, if a company sets AQL levels as Critical: 0%, Major: 2.5% and Minor: 4.0% and the batch size is 5000 units, an inspector may select 200 units as a sample size. If the number of major defects exceeds 10 units, the batch fails the inspection.
Why AQL is Important for Businesses
1. Ensures Product Quality
AQL helps maintain a consistent quality standard by setting predefined defect limits, reducing the risk of receiving defective goods.
2. Balances Quality and Cost
Instead of inspecting every unit, AQL-based sampling allows businesses to identify quality issues while keeping inspection costs manageable.
3. Reduces Customer Complaints and Returns
By maintaining strict AQL standards, businesses can minimize defects, leading to fewer returns, refunds and negative reviews.
4. Complies with International Standards
Many global retailers and brands require manufacturers to comply with AQL-based inspections, making it a crucial quality control practice in international trade.
5. Strengthens Supplier Accountability
AQL inspections encourage suppliers to improve their production processes and adhere to quality expectations, reducing risks in the supply chain.
Common Challenges in AQL Inspections
1. Defining Appropriate AQL Levels
Different products and industries require different AQL levels. Setting too strict an AQL can increase production costs, while a lenient AQL may compromise quality.
2. Supplier Resistance
Some suppliers may not agree with strict AQL standards, leading to disputes or production delays.
3. Human Error in Inspections
Inspectors may misclassify defects or make subjective judgments, leading to inconsistencies in results.
4. Sampling Limitations
Since AQL relies on random sampling, defects in uninspected units may still reach customers, posing potential risks.
Read Frequently Asked Questions about AQL
How Testcoo Can Help with AQL-Based Inspections
At Testcoo, we specialize in third-party product inspections to help businesses implement effective AQL-based quality control strategies. Our services include:
- Initial Product Check (IPC): IPC is done to check the quality at about 10-30% product finished stage
- During Production Inspections (DUPRO): DUPRO helps in detecting issues early in production.
- Supplier Audits: Evaluating supplier reliability and production processes via supplier audits.
- Customized AQL Inspections: Tailored quality control plans based on specific AQL levels.
- Detailed Inspection Reports: Providing comprehensive reports with defect classifications and recommendations.
By partnering with Testcoo, businesses can ensure compliance with international quality standards, reduce risks and enhance customer satisfaction.
AQL is a crucial tool in product inspections, ensuring that only acceptable-quality products reach the market. By implementing AQL standards, businesses can balance cost and quality while minimizing the risk of defective products. Working with a trusted third-party inspection provider like Testcoo can further enhance quality assurance and supply chain reliability.
If you need professional AQL-based product inspections, contact Testcoo today and safeguard your product quality with confidence!
Free Sample Report Performance Quality Control
Download a sample report to keep control of your supply chain!
Featured Articles
 AQL Table | How to Read It
AQL Table | How to Read It TOP 10 Common Defects in Garments Quality Inspection
TOP 10 Common Defects in Garments Quality Inspection Product Packaging and Shipment Label requirements for Amazon FBA
Product Packaging and Shipment Label requirements for Amazon FBA What Is ASTM-F2413-18? Protective Footwear Standard
What Is ASTM-F2413-18? Protective Footwear Standard How to Conduct Third-Party Quality Control Inspections for Electric Scooters
How to Conduct Third-Party Quality Control Inspections for Electric Scooters SMETA Audit-What is SMETA Audit?
SMETA Audit-What is SMETA Audit? TESTCOO Supplier Verification/Certification Service SLCP, Higg FEM, GRS, GOTS
TESTCOO Supplier Verification/Certification Service SLCP, Higg FEM, GRS, GOTS Quality Control Inspection Company in China
Quality Control Inspection Company in China What is Quality Inspection? A Complete Guide
What is Quality Inspection? A Complete Guide Guidelines for Product Inspection in India
Guidelines for Product Inspection in India
Category
- Production Inspection Service
- Factory Audit
- Softline Inspection
- Hardline Inspection
- Electrics Inspection
- Certification
- Checklist
- Manufacturers
- Quality Assurance Basics
- Products Recall
- AQL
- Guidence and Standard
- News
- Supplier Management
- Amazon
- Protective Equipment
- e-commerce quality control
- Indian Manufacturing
- Soft Goods Quality Control
- Supply Chain Management
- Supply Chain Resilience
- E-Commerce Quality Control
- ISO 2859
- Supply Chain Optimization
- Garment Industry
- Higg Index




