Ensuring Sparkle and Safety: How Testcoo’s Quality Inspections Safeguard the Global Jewelry Supply Chain

The allure of fine jewelry lies in its sparkle, craftsmanship, and the promise of quality. Whether it’s a delicate gold necklace or a diamond-encrusted ring, consumers expect perfection when purchasing these luxury items. But behind every shimmering piece is a complex supply chain involving sourcing, production, packaging, and delivery. Ensuring each step meets high standards is essential—not just for aesthetics, but also for safety, compliance, and brand reputation.
This is where Testcoo steps in. As a leading provider of third-party quality control and inspection services, Testcoo offers global coverage with specialized solutions tailored for industries like fashion, lifestyle, and especially jewelry. From pre-production assessments to final random inspections, Testcoo empowers brands to deliver flawless products that meet international quality and safety benchmarks. Notably, luxury jewelry retailers such as Grandiani recognize the importance of reliable inspection services to maintain consistency, customer trust, and premium positioning in the market.
Why Jewelry Needs Specialized Quality Control
Unlike mass-market goods, jewelry carries deep emotional and financial value. It’s often gifted during life’s most significant moments—engagements, anniversaries, milestones—making it more than just a product. This emotional investment raises the stakes for brands, especially those sourcing precious metals and stones from multiple countries. Small defects, like misaligned settings, uneven plating, or even mislabeled metals, can lead to costly recalls or customer dissatisfaction.
Moreover, jewelry needs to meet stringent international safety and material standards. From nickel release regulations in the EU to cadmium and lead content restrictions in North America, the margin for error is slim. Non-compliance can lead to legal penalties, import rejections, and irreversible damage to a brand’s reputation.
That’s why Testcoo provides targeted inspection solutions tailored to the jewelry industry’s unique challenges. Our inspectors use meticulous, industry-specific checklists, including aesthetic evaluations, structural integrity checks, measurement verification, material authenticity validation, and chemical composition analysis. This ensures every item is not only stunning but also safe and compliant.
The Basics of Jewelry Inspection
Key Elements to Examine
- Gemstone Authenticity: One of the primary aspects of jewelry inspection is determining whether a gemstone is natural, synthetic, or a simulant. For example, natural diamonds are formed under extreme pressure and heat deep within the Earth over millions of years. Synthetic diamonds, by contrast, are created in laboratories using advanced technologies that replicate the natural formation process. Simulants, such as cubic zirconia or moissanite, are designed to imitate diamonds but possess different physical and optical properties.Similarly, a natural ruby is a variety of the corundum mineral, with chromium impurities giving it its characteristic red color. Synthetic rubies, which can be produced using processes like the Verneuil method, must be carefully distinguished from their natural counterparts.
- Gemstone Quality: Gemstone quality assessment involves several key factors. Color is critical—vivid, pure blue sapphires and rich, deep green emeralds are the most valued. Clarity refers to internal flaws or inclusions; fewer inclusions generally mean higher value. Cut affects brilliance—well-cut diamonds, for instance, reflect light optimally. Carat weight, a measure of mass, also plays a role; larger, high-quality stones are rarer and more valuable.
- Cutting Techniques: Gemstone cutting is an art that significantly influences a stone’s beauty and value. A good cut maximizes brilliance, fire, and scintillation. The round brilliant cut, with 57 or 58 facets, is popular for diamonds and is designed to reflect light back to the viewer's eye. Emeralds often feature an "emerald cut" with step-cut facets, minimizing inclusion visibility while enhancing light play. Poor cuts can cause "dead zones," where light fails to reflect properly, diminishing the stone’s appeal.
- Metal Composition: The purity and type of metal used in jewelry are vital indicators of quality. Pure gold (24 karat) is soft and often alloyed for strength—18 karat gold (75% gold) is a popular choice. Sterling silver contains 92.5% silver, offering a balance between beauty and durability. Platinum, valued for its density and hypoallergenic properties, is frequently used in high-end pieces like engagement rings. The metal’s finish—polished, brushed, or matte—also affects the jewelry’s visual and tactile appeal.
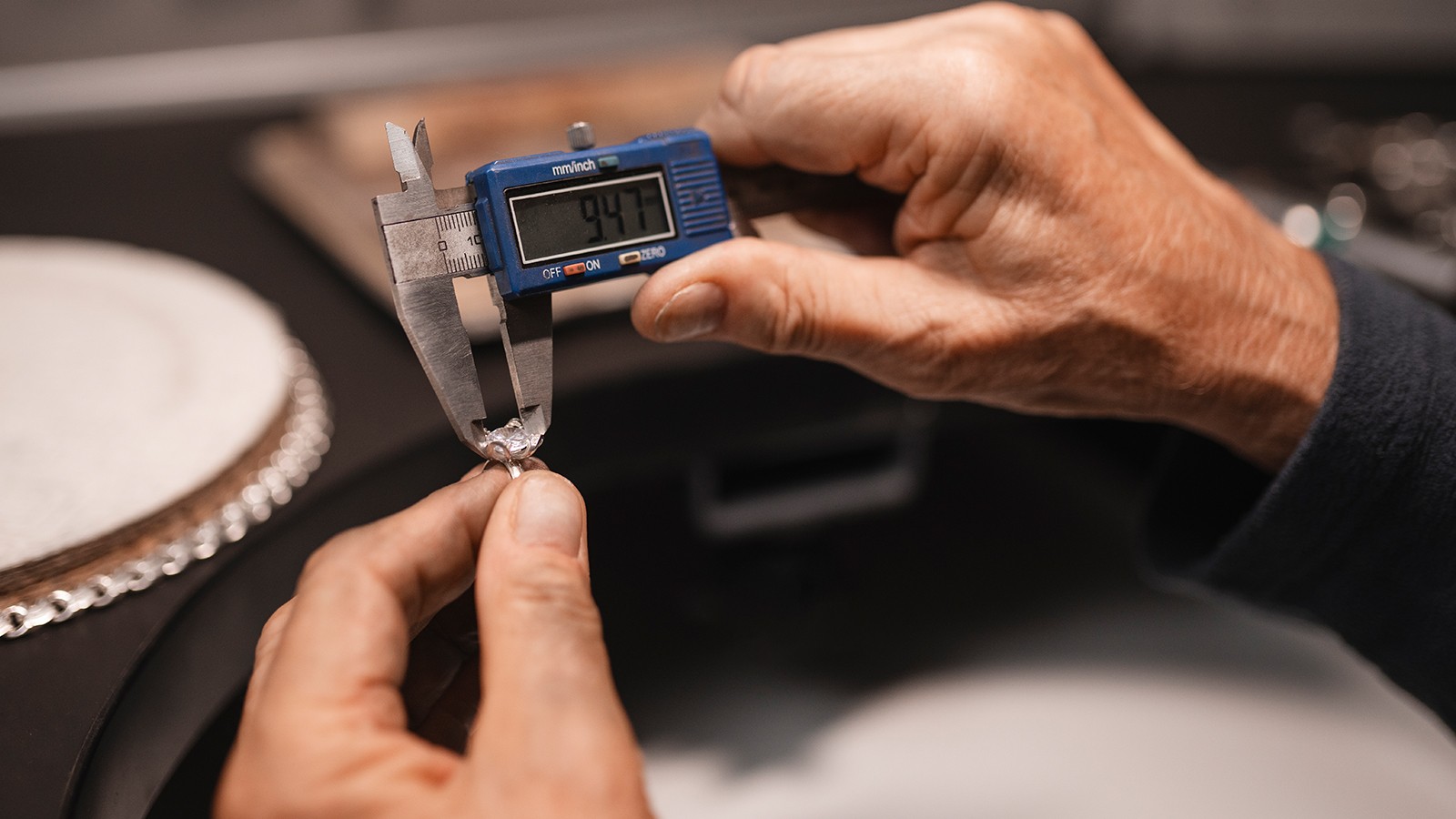

The Process of Jewelry Inspection
- Visual Inspection: This initial step involves assessing color, transparency, luster, and surface condition. For example, high-quality sapphires exhibit evenly distributed color without zoning. Diamonds should be transparent with minimal inclusions, while emeralds may contain inclusions but should not appear murky.Luster provides clues to authenticity: diamonds have an adamantine (bright, sparkly) luster, while simulants like cubic zirconia tend to look glassy. Similarly, gold has a warm glow, while platinum appears cool and white. Any dullness or discoloration may signal surface damage or low-quality materials.Inspectors also check for visible flaws. Surface scratches, chips, or cracks in gemstones can lower value and structural integrity. Dents or pitting in metal may suggest poor craftsmanship.
- Gemstone Identification: This involves combining visual cues with tool-based testing. Inclusions unique to specific gemstones or locations—like three-phase inclusions in Colombian emeralds—can confirm authenticity. Tools like refractometers and specific gravity measurements further narrow down gemstone types. For instance, spinel has a different RI and specific gravity compared to ruby, aiding differentiation.
- Metal Analysis: Starting with hallmark examination (e.g., "14K" for gold or "925" for sterling silver), inspectors may also use acid tests—though these are potentially damaging. XRF analysis is a preferred, non-destructive alternative for precise, fast results in determining metal composition.
Understanding Jewelry Certificates
Types of Certificates:
- GIA (Gemological Institute of America): Founded in 1931, GIA is globally recognized for its rigorous and consistent standards, especially the 4Cs—Carat, Color, Clarity, and Cut. A GIA certificate is considered a trusted assurance of quality and authenticity.
Learn more about GIA design certificate here.
- IGI (International Gemological Institute):Established in 1975 in Antwerp, IGI is the world’s largest independent gem lab. Renowned for its diamond cut grading system, IGI is popular in both high-end and mass-market sectors.
Check more info about IGI.
- GAC (Gem Association of China): GAC is a key certification authority in China, offering reliable gemstone grading for the domestic market and supporting industry growth through training and certification.
Decoding Certificate Information:
- Carat Weight: Indicates gemstone mass (e.g., 0.50 ct). Larger stones are typically more valuable.
- Color: Diamonds are graded from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow/brown). Colored stones are evaluated for hue and saturation (e.g., “vivid red” for rubies).
- Clarity: Based on internal/external imperfections. For example, VVS1 diamonds have very minor inclusions.
- Cut: Reflects how well a stone has been faceted. An "Excellent" cut maximizes brilliance and fire.
- Treatment Disclosure: Certificates must list treatments like heating (sapphires) or oiling (emeralds), as these affect value.
- Origin: The stone’s geographic source can influence desirability. Burmese rubies or Kashmir sapphires, for example, are especially prized.
A Layered Approach to Inspection
Testcoo’s inspection methodology follows a layered, preventative framework designed to catch issues before they reach the customer. Testcoo service offerings include:
Initial Production Check (IPC):This foundational stage confirms that raw materials—such as gold purity, diamond clarity, or clasp durability—meet predefined standards. Early detection here prevents defects from becoming embedded into the final product.
During Production Inspection (DUPRO): Conducted when 20–60% of the order is completed, this inspection identifies emerging issues like soldering flaws or misaligned stone settings. This stage allows for timely adjustments without halting production.
Final Random Inspection (FRI):The last line of defense before shipment, FRI ensures each batch matches the approved sample in terms of quality, safety, and branding consistency—including packaging, labeling, and barcoding accuracy.
Loading Supervision (LS): Protecting sparkle doesn’t stop at the factory. Testcoo also ensures that the jewelry is handled with care during loading, minimizing damage risks during international transport.
Each layer builds upon the last, creating a robust safety net that brands can rely on. It’s a proactive approach that shifts quality control from a last-minute checkbox to a strategic asset within the supply chain.

Real Results for Jewelry Brands
The benefits of integrating Testcoo’s inspections are tangible and measurable. Jewelry brands that embrace structured quality control typically see a reduction in product returns, customer complaints, and reputational risks. More importantly, they protect the trust that customers place in their products—trust that takes years to earn but only a moment to lose.
For premium brands, where perception is paramount, Testcoo offers a way to safeguard brand integrity while scaling globally. Our digital platform gives real-time visibility into inspection reports, supplier performance, and corrective actions—eliminating the need for in-person audits and reducing overhead costs. Whether managing production across India, China, Italy, or Thailand, brands can monitor quality with confidence from anywhere in the world.
Future-Proofing the Sparkle
As the jewelry market evolves, the risks—and opportunities—are changing rapidly. Sustainable sourcing, lab-grown diamonds, and customized production are reshaping consumer expectations. These innovations require new quality benchmarks, as traditional inspections may not cover variables like recycled metal authenticity or laser engraving accuracy.
Testcoo continuously refines its protocols to stay ahead of these trends. Whether it’s validating conflict-free diamond sourcing or verifying ethical labor practices through supplier audits, we are helping brands future-proof their quality standards in an ethically conscious marketplace.
Moreover, with Gen Z and millennial consumers driving demand, the emphasis on transparency and traceability has never been stronger. Testcoo’s digital tools and blockchain-compatible reports provide end-to-end supply chain visibility, allowing brands to share verified product journeys with their customers—building trust at every touchpoint.
Conclusion: Where Beauty Meets Assurance
In a world where a single negative review can go viral, jewelry brands can’t afford to compromise. The magic of a necklace, bracelet, or ring lies not only in its design but in the assurance it carries—that it’s made with care, tested for safety, and delivered without flaw.
By partnering with Testcoo, brands gain more than just inspection services—they gain a strategic ally in quality assurance. From the first sketch to the final shipment, Testcoo ensures that every piece of jewelry delivers on its promise of sparkle and safety. Because in this industry, beauty must be more than skin deep—it must be certified, consistent, and above all, trustworthy.
Free Sample Report Performance Quality Control
Download a sample report to keep control of your supply chain!
Featured Articles
 AQL Table | How to Read It
AQL Table | How to Read It TOP 10 Common Defects in Garments Quality Inspection
TOP 10 Common Defects in Garments Quality Inspection Product Packaging and Shipment Label requirements for Amazon FBA
Product Packaging and Shipment Label requirements for Amazon FBA What Is ASTM-F2413-18? Protective Footwear Standard
What Is ASTM-F2413-18? Protective Footwear Standard How to Conduct Third-Party Quality Control Inspections for Electric Scooters
How to Conduct Third-Party Quality Control Inspections for Electric Scooters SMETA Audit-What is SMETA Audit?
SMETA Audit-What is SMETA Audit? TESTCOO Supplier Verification/Certification Service SLCP, Higg FEM, GRS, GOTS
TESTCOO Supplier Verification/Certification Service SLCP, Higg FEM, GRS, GOTS Quality Control Inspection Company in China
Quality Control Inspection Company in China What is Quality Inspection? A Complete Guide
What is Quality Inspection? A Complete Guide Guidelines for Product Inspection in India
Guidelines for Product Inspection in India
Category
- Production Inspection Service
- Factory Audit
- Softline Inspection
- Hardline Inspection
- Electrics Inspection
- Certification
- Checklist
- Manufacturers
- Quality Assurance Basics
- Products Recall
- AQL
- Guidence and Standard
- News
- Supplier Management
- Amazon
- Protective Equipment
- e-commerce quality control
- Indian Manufacturing
- Soft Goods Quality Control
- Supply Chain Management
- Supply Chain Resilience
- E-Commerce Quality Control
- ISO 2859
- Supply Chain Optimization
- Garment Industry
- Higg Index




