AQL Complete FAQ Guide: AQL 0.65, 1.5, 2.5, 4.0 & AQL Sampling Explained

If you want to learn everything about AQL, this article will provide all the answers.
From basic definitions, importance, standards, to other key terms related to AQL.
Continue reading to learn more.
What does AQL stand for?
According to ISO 2859-1, AQL stands for Accepted Quality Limit (Accepted Quality Limit).
What does AQL mean?
The Acceptable Quality Level (AQL) refers to the maximum number of defects that are acceptable in a product.
During sampling quality inspections of products, AQL serves as a baseline to determine whether to accept or reject a batch of goods.
This is an internationally recognized system for assessing the quality of an entire batch of goods based on the percentage of sample quality.
What is the importance of AQL in international shipping?
Quality control in international shipping can be stressful but is crucial.
You want to receive the best possible products from your suppliers with no defects.
At the same time, you may lack the budget and manpower to inspect each product individually before shipment.
This is where AQL sampling comes in handy to ensure you get value for your money.
By conducting quality inspections at the production site, you can confirm the quality of the goods before shipment.
AQL sampling saves time because you do not need to inspect the entire batch.
Conducting 100% quality inspections would be time-consuming and costly.
Unlike random sampling methods (e.g., sampling 10% of the total order), AQL sampling provides a unique random process that ensures accurate and unbiased results.
What is the importance of conducting AQL inspections?
Inspections are crucial to ensuring that suppliers consistently provide high-quality goods that align with your budget.
AQL is preferred in most cases because it fairly reflects the quality of the entire order.
Conducting AQL inspections offers the following advantages:
- You want to inspect order quality while also ensuring the order is shipped promptly.
- By inspecting through sampling, you can save time while maintaining quality.
- 100% inspection is costly and requires more manpower.
- Choosing AQL sampling saves costs without compromising inspection results.
- AQL sampling provides results directly related to the required quality inspection.
This is a direct method based on acceptance or rejection.
If defects in the sample exceed the set limit, the order will be automatically rejected.
What are the types of AQL?
AQL is divided into two types, each with different levels.
General Inspection Level
The General Inspection Level is the most widely used AQL type, suitable for situations where quality inspection has minimal impact on the product and time and resources are not constrained.
It includes:
GI Inspection Level
The GI Inspection Level is the most economical and time-efficient.
It selects the smallest sample size to analyze the quality of the entire batch of supplies.
GI is suitable for collaborating with suppliers with a good supply history or when you do not wish to bear the costs and time of a full inspection.
GI levels use set standards to draw conclusions in quality inspection.
As an importer, you can set the quality level for minor defects to 4 and severe defects to 0.
This means that if defective products exceed 4% of the sample, the product will be rejected.
The higher the acceptance quality level you set, the higher the tolerance for defective products during transportation.
GII Inspection Level
GII is also known as the normal sample size.
Most importers use this level because it covers the main product samples at a lower cost.
It is suitable for first-time customers or new orders from the same supplier.
Through GII, you can assess the quality of the first order.
If the same quality level is used, you should increase the acceptance level because the sample size has increased.
GIII Inspection Level
From a trend perspective, GII takes the longest time because it includes the largest sample size.
However, GII inspection is crucial as it provides the most representative quality results.
GIII is applicable for suppliers with poor reputations, those consistently supplying defective products, first-time suppliers, or products with high value that directly impact human health.
However, GIII is the most time-consuming and should only be used if you are willing to spend more time and bear the sampling labor costs.
Special Inspection Level
Special inspection levels are used when quality verification is required but time and resources are limited.
It is divided into four categories, each with specific AQL acceptance and rejection values.
What do severe, major, and minor defects in AQL refer to?
These are defect classifications in AQL sampling.
Minor Defects
Minor defects refer to products with the smallest deviation from expected quality.
Such products can be accepted because consumers are still willing to purchase or use them despite minor defects.
For example, a radio ordered may be missing one or two screws but functions normally.
Minor defects have a higher AQL (4.0), meaning a lower rejection rate.
Major defects
Major defects refer to products that fail to meet quality standards during production.
Such products have a higher probability of being rejected in the market.
For example, a television may function but be missing a remote control.
Major defects have a slightly higher rejection probability (2.5).
Critical defects
Critical defects typically occur in specific industries where a single error can cause significant damage.
Therefore, critical defects are unacceptable.
If a single critical defect is detected during quality inspection, the entire batch will be rejected.
For example, a phone that continues to heat up when placed in a pocket.
Such defects affect health, and the AQL is set to 0.
Related reading: Acceptable Quality Level (AQL)
How to calculate AQL?
AQL has evolved since its initial design in the 1920s.
Its objective is to ensure that products have a 95% probability of being accepted by customers.
There are no predefined default AQL limits.
If an order does not allow any defects, the critical value (0) can be selected; for consumables, minor defects can be set to 2.5.
In cases where consumers have less stringent quality requirements, it is recommended to set major defects to 4.
You can use an online AQL calculator to determine the sample size.
Enter the batch size, select the inspection type (general or special), then choose the inspection level and AQL.
The tool will automatically generate the acceptance point and rejection point.
What is the standard AQL?
There is no uniform standard AQL applicable to all products.
It depends on the specific needs of the customer and supplier.
Setting a lower AQL may lead to the supplier rejecting the order, while a higher AQL may result in accepting more defective products.
You should set AQL limits based on the market you are in and the type of products you are ordering.
What does AQL 2.5 mean?
An Acceptable Quality Level of 2.5 means the buyer is willing to accept a defect rate of 2.5% in the sample.
If the number of defective products exceeds 2.5% of the total order quantity, the order is rejected; if it is below 2.5%, the order is accepted.
Related reading: 7 Major Onsite Tests Checklist for Disposable Latex Gloves Inspection in China
What does AQL 4.0 mean?
AQL 4.0 provides the greatest flexibility in accepting defects.
It indicates the total number of defective products the customer is willing to accept.
AQL 4 is used for minor defects or situations where consumers will still purchase the product even if defects are found.
What does AQL 1.5 medical grade mean?
AQL 1.5 means that if the defective product rate in an order exceeds 1.5%, the order will be rejected.
Additionally, AQL 1.5 informs suppliers that orders will only be accepted if the total defect rate is below 1.5%.
What does AQL 0.65 mean?
After sampling inspection, the total defect rate of the sample is converted into the defect probability of the entire batch.
AQL 0.65 means that the customer will only accept orders where the defect rate of the entire batch is below 0.65%.
What is PPM? How is it related to AQL?
PPM stands for parts per million and is commonly used in manufacturing to assess the number of defects per million products.
Assuming that out of 1,000 items in a batch, 25 are defective, the defect rate is 25/1,000 = 0.025.
In this case, the PPM is 0.025 × 1,000,000 = 25,000 ppm, meaning there are 25,000 defective products per million units.
The significance of PPM lies in showing the actual probability of receiving defective products from a single manufacturer when increasing or decreasing order quantities.
When should AQL sampling be used in international shipping?
In international shipping, you typically collaborate with overseas suppliers.
To ensure only high-quality products are shipped, a reliable quality inspection method must be adopted.
Other quality inspection methods may involve 100% inspection, but these are costly and time-consuming, so AQL sampling should be chosen.
AQL sampling is effective in the following situations:
- The supplier uses automated mass production. AQL is used to ensure that each batch of products meets the quality threshold.
- The supplier's historical performance is unstable and cannot guarantee 100% quality. AQL can verify quality and make decisions before shipment.
- When handling large orders, conventional quality inspection is time-consuming and expensive.
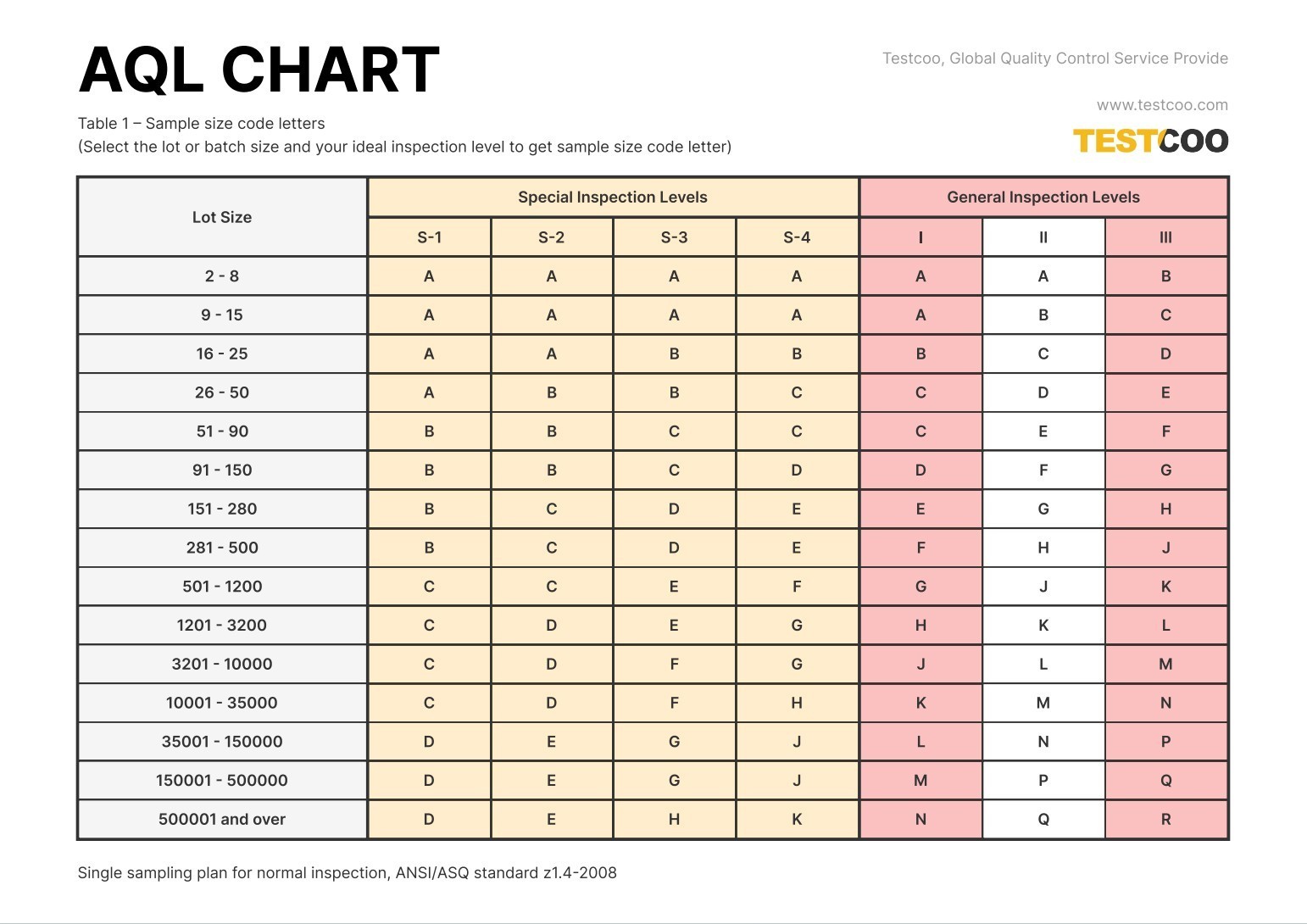
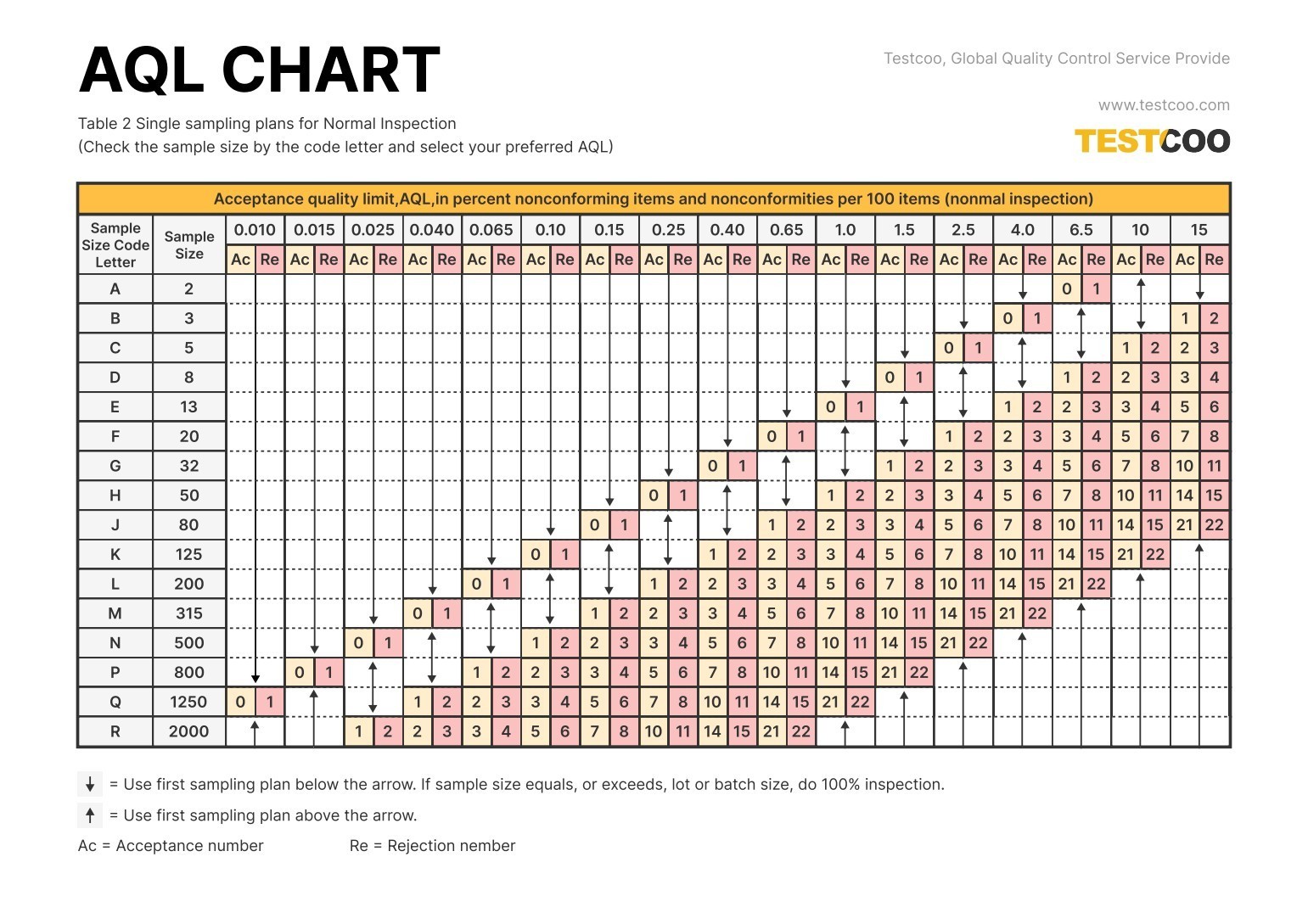
How to read the AQL sampling table?
The AQL sampling table may be confusing for first-time users, but with experience, you will understand and master its usage.
The AQL sampling table is divided into two parts:
- Sample size code alphabetical table: Includes batch size, three general inspection levels, and four special inspection levels. Batch size provides the order quantity range, and inspection levels correspond to the applicable AQL.
↵
↵
- In the first table, select the corresponding category and AQL based on the order quantity.
- Below the column containing the order quantity, record the corresponding AQL code letter.
- In the second table, locate the sample size based on the code letter and view the acceptance and rejection values for the AQL in the same row.
If the number of defects in the sample exceeds the rejection value, the entire batch is rejected.
Related Reading: Understanding AQL in Product Inspections: A Complete Guide to Quality Control
What is a C=0 Sampling Plan?
A C=0 sampling plan is used for sensitive products that require zero defects.
Under this plan, the order is accepted only if no defects are found in the sample; if one defect is found, the entire batch is rejected.
The C=0 plan aims to protect consumers of products related to health and safety, requiring orders to meet 100% quality standards.
What is routine inspection?
Routine inspection, also known as Level II inspection, is the default inspection type and applies to over 90% of quality control scenarios.
It is used when order quality is normal, offering either high or low discrimination, making it an ideal choice.
Is AQL superior to routine inspection?
AQL determines whether the entire batch meets the minimum quality standards through sampling, while normal inspection is only used when defects are not expected.
Therefore, AQL is more reliable, and its results accurately reflect the quality of the entire batch.
What is AQL in textiles?
AQL is used in the textile industry to define the maximum acceptable percentage of defects, reflecting the quality level of textiles that meet consumer demands.
The minimum AQL may vary among different buyers, with no uniform standard.
AQL in the textile industry is divided into four categories:
- Minor defects (typically 4%, acceptable to consumers)
- Major defects (typically 2.5%, consumers would not consider purchasing)
- Critical defects (no range, the product must be 100% defect-free)
- Minor defects (0.65%, typically detected during manufacturing)
What is LTPD?
The Lot Tolerable Defect Rate (LTPD) refers to the quality level that a sampling plan typically rejects.
It indicates that the probability of accepting the defect rate is 10%, and the probability of rejection is 90%.
LTPD reflects the confidence level of the sampling plan results.
What is the difference between AQL and LTPD?
AQL is the maximum defect rate acceptable to the customer before shipment, while LTPD is the quality level at which the sampling plan typically rejects the product.
LTPD indicates that, out of every 100 products, the sampling plan accepts a defect rate of 10% and rejects a defect rate of 90%.
How is the sample size for AQL sampling determined?
The sample size refers to the number of representative products in quality inspection.
Determine the sample size using the charts in the ANSI Z1.4-2013 standard:
- In the first table, locate the code letter based on the order quantity and inspection level.
- In the second table, obtain the sample size based on the code letter.
Related reading: AQL Sampling Inspection Explained: How to Read Tables and Design a QC Plan
What are the alternative methods for AQL quality inspection?
Depending on the industry and destination country, quality inspection may require other methods:
- Confidence/reliability calculations
- AOQL
- Attribute data
- Squeglia's C=0
- OC curve
- ANSI Z1.4
How to develop an AQL sampling plan?
An AQL sampling plan is a detailed sampling execution plan that must include the following steps:
- Determine the evaluation characteristics, value range, and expected results
- Develop a sampling schedule and quantity plan
- Select the sample size
- Design the data storage method
- Assign sampling team responsibilities
- The plan must be approved by the team before implementation.
What is the AQL level?
The AQL level is the minimum quality standard that must be met before an order is accepted, specifying the maximum acceptable defect quantity.
How to select AQL limits for a product?
When selecting AQL limits, consider:
Market
High-end markets with intense competition require strict quality control, so lower AQL levels (e.g., 1, 1.5, 0.2) should be chosen.
Lower-priced markets can be relaxed to 2.5 or 4.
User risk
Industries involving health or safety (e.g., pharmaceuticals, transportation) require strict AQL (≤1%) or even zero defects.
Can AQL guarantee zero defects?
No.
All manufacturing processes may contain defects, and AQL sampling only saves time and costs.
Due to sampling probability limitations and the limitations of quality inspection checklists, zero defects cannot be guaranteed. It is recommended to combine with other quality inspection methods.
Can defective batches be salvaged after AQL sampling?
It depends on the situation.
If defects exceed the AQL limit, the entire batch is rejected.
If the AQL is met but defects still exist, depending on the agreement with the supplier, options include retaining, replacing, or deducting payment.
Can sampling plans be customized?
Yes, but this may increase the risk of defective products passing. It is recommended to follow standard sampling methods to ensure reliability of results.
How do you determine the AQL sample size?
Refer to the standard AQL table:
- Select the AQL category (general or special).
- Locate the order quantity in the batch size row.
- Obtain the code letter based on the AQL.
- Match the sample size in the second table.
Can products from the same distribution channel use the same AQL limit?
Yes, but it is not recommended.
Limits should be adjusted based on manufacturing processes and component variations, typically selecting 0, 1.5, and 2.5 to correspond to severe, major, and minor defects, respectively.
Is AQL sampling only applicable to finished products?
No. AQL sampling is applicable to any product that can be classified as “合格” or “defective,” and can also be used for inventory or invoice verification.
What is RQL?
The Rejection Quality Level (RQL) is the highest defect rate a customer is willing to accept, representing the upper limit of risk consumers are willing to accept for a specific defect rate.
How is RQL calculated?
RQL is the defect rate consumers wish to reject with a high probability (β). For example, if the consumer's risk α is 0.10 and RQL is 8%, then when an order has an 8% defect rate, there is a 10% probability it will be accepted.
What is the relationship between AQL and RQL?
AQL determines the acceptance criteria for the sampling plan, while RQL determines the rejection criteria. Both parties must agree on the maximum acceptable defect rate.
How should defects exceeding AQL be handled?
First, verify the order quantity and, based on the agreement, choose to return the entire batch for replacement or replace only the defective products.
Should the buyer deduct payment from the manufacturer?
If the product fails the AQL inspection, the supplier is responsible for replacement. If further inspection is required after replacement, the costs are borne by the supplier.
What is a special inspection level?
A special inspection level is used in the following situations:
- Inspection results are consistent across the entire batch
- Inspection time is too long or costs are too high
It is recommended to consult with the inspection company before deciding whether to continue importing.
What is the difference between a special inspection level and a general inspection level?
The general inspection level uses a larger sample size, while the special inspection level uses a smaller sample size. The former is used for diverse inspections, while the latter is used for homogeneous products, resulting in lower costs and shorter inspection times.
What is an Operational Characteristic (OC) curve?
An OC curve is a chart that illustrates the relationship between order acceptance probability and defect rate. When the defect rate is 0%, the order acceptance probability is 100%.
Conclusion
AQL sampling stands as a cornerstone in international trade quality control, functioning far beyond a simple inspection tool. It establishes a balanced framework for managing quality risks and inspection costs, ensuring that product batches meet predefined standards without the inefficiency of full inspections. By setting clear acceptable defect limits and following systematic sampling procedures—whether for general or special inspection levels—importers and exporters can confidently assess product quality, safeguard consumer interests, and maintain smooth supply chain operations.
Whether you are a buyer seeking to avoid substandard shipments or a supplier striving to uphold consistent quality, leveraging AQL sampling and partnering with seasoned inspection experts will enhance your competitiveness in the global market. To support your quality control efforts across every stage of production and shipping, including AQL implementation and beyond, consider trusted service providers like Testcoo.
Free Sample Report Performance Quality Control
Download a sample report to keep control of your supply chain!
Featured Articles
 AQL Table | How to Read It
AQL Table | How to Read It TOP 10 Common Defects in Garments Quality Inspection
TOP 10 Common Defects in Garments Quality Inspection Product Packaging and Shipment Label requirements for Amazon FBA
Product Packaging and Shipment Label requirements for Amazon FBA What Is ASTM-F2413-18? Protective Footwear Standard
What Is ASTM-F2413-18? Protective Footwear Standard How to Conduct Third-Party Quality Control Inspections for Electric Scooters
How to Conduct Third-Party Quality Control Inspections for Electric Scooters SMETA Audit-What is SMETA Audit?
SMETA Audit-What is SMETA Audit? TESTCOO Supplier Verification/Certification Service SLCP, Higg FEM, GRS, GOTS
TESTCOO Supplier Verification/Certification Service SLCP, Higg FEM, GRS, GOTS Quality Control Inspection Company in China
Quality Control Inspection Company in China What is Quality Inspection? A Complete Guide
What is Quality Inspection? A Complete Guide Guidelines for Product Inspection in India
Guidelines for Product Inspection in India
Category
- Production Inspection Service
- Factory Audit
- Softline Inspection
- Hardline Inspection
- Electrics Inspection
- Certification
- Checklist
- Manufacturers
- Quality Assurance Basics
- Products Recall
- AQL
- Guidence and Standard
- News
- Supplier Management
- Amazon
- Protective Equipment
- e-commerce quality control
- Indian Manufacturing
- Soft Goods Quality Control
- Supply Chain Management
- Supply Chain Resilience
- E-Commerce Quality Control
- ISO 2859
- Supply Chain Optimization
- Garment Industry
- Higg Index




