Camping Tent Inspection: Requirements and Methods You Must Know

↵
In the realm of outdoor activities, a camping tent serves as a crucial sanctuary. Whether you're an avid hiker scaling mountains, a nature lover embarking on a long-distance trek, or a family seeking a weekend getaway in the woods, the tent is your temporary home away from home. It provides shelter from the elements, be it a sudden downpour, scorching sun, or chilly wind. A well-made tent can transform an uncomfortable outdoor experience into a cozy and enjoyable adventure, while a poorly constructed one can lead to leaks, collapses, and overall disappointment.
Therefore, understanding the inspection requirements and methods for camping tents is of utmost importance. It ensures that the tent you purchase or use meets the necessary quality standards, guaranteeing your safety and comfort during outdoor escapades. By conducting thorough inspections, manufacturers can uphold high-quality production, and consumers can make informed purchasing decisions. This article delves into the detailed requirements and practical methods for inspecting camping tents, aiming to provide a comprehensive guide for all parties involved in the camping tent industry.
General Requirements for Camping Tents
- Fabric-Related Requirements
The fabric of a camping tent is its first line of defense against the elements. There are multiple aspects to consider in terms of fabric requirements.
- Tear Strength: The tear strength of the fabric is crucial as it determines the tent's ability to withstand forces that could cause it to rip. For example, when branches might scrape against the tent during windy conditions or if there's accidental snagging. According to ISO standards, the tear strength of the fabric (both with and without coating) should be at least 25 N. This ensures that the fabric can endure normal wear and tear during outdoor use without easily tearing apart.
You can learn more about the ISO fabric strength standards in detail at ISO/TC 38 - Textiles.
- Tensile Strength: The tensile strength measures how well the fabric can resist being pulled apart. A camping tent often experiences tension when it's set up, especially in windy weather. The ISO standard requires that the tensile strength of the fabric (coated or uncoated) should reach 500 N. This high-strength requirement ensures that the tent can maintain its structural integrity under the stress of being stretched.
- Water Resistance: Outdoor activities often expose tents to rain, so water resistance is a vital property. The fabric should have a sufficient hydrostatic head to prevent water from seeping through. In accordance with ISO standards, the fabric should be able to withstand a water pressure of 30 kPa without water penetration. This ensures that campers stay dry even during moderate to heavy rainfall.
- Weather Resistance: The tent fabric needs to endure various weather conditions over time, including sunlight, wind, and temperature changes. The weather resistance of the fabric is evaluated by its color fastness and durability under simulated weather conditions. It should have a color fastness (wet friction) of at least 4 levels and a weather resistance (compared with blue wool standards) of 4 levels. This ensures that the fabric doesn't fade quickly and maintains its physical properties over time when exposed to the elements.
- Size Stability
Size stability is another important factor. A tent that shrinks or expands significantly after exposure to water or changes in temperature can be a nuisance to set up and use. According to the ISO 7771 standard, when tested with a 2-hour test cycle, the size change of the fabric should not exceed ±3%. This means that whether the tent gets wet during a rainstorm or is exposed to high-humidity environments, its dimensions will remain relatively stable, ensuring that it can be easily assembled and disassembled and that the components fit together as designed.
- Flammability
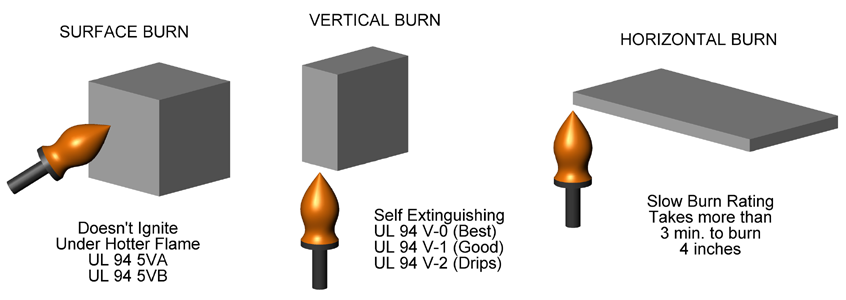
If the manufacturer claims that the tent fabric has flame-retardant properties, it must be tested according to ISO 6941:2003 test procedure A.
- For the outer tent: When tested with a 10-second ignition time using surface ignition, no marked lines should be burned off, there should be no burning debris, no flames should appear on each vertical edge of the sample, the after-flame time of each sample should not exceed 10 seconds, and the average after-flame time should not exceed 6 seconds. This helps to prevent the outer tent from quickly catching fire and spreading the flame in case of a fire source nearby, such as a campfire getting out of control.
- For the inner tent: When tested in the same way, no marked lines should be burned off, no more than 2 samples should have burning debris, no flames should appear on each vertical edge of the sample, the after-flame time of each sample should not exceed 20 seconds, and the average after-flame time should not exceed 12 seconds. In case of an internal fire risk, such as a lit candle accidentally falling over inside the tent, these requirements ensure that the inner tent won't contribute significantly to the spread of the fire. If a sample fails the test, it should be retested once. If the second test still fails, the fabric is considered to have not passed the test.
- For the groundsheet: According to ISO 6925, when tested, the combustion radius should be less than 35 mm. This ensures that in case of a fire on the ground, the groundsheet won't rapidly spread the fire, providing an additional layer of safety for the tent and its occupants.
↵
Component Requirements
Tent Stands: Metal components must show only slight discoloration after testing. Plated/coated stands should have corrosion penetration no more than 0.5 mm after ISO 9227 testing. Components should be marked for easy assembly, and combined components must remain stable under twice their weight. Tubular joints should be twice the outer diameter in length.
You can find more information about tent stand manufacturing standards at https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/en/#iso:std:iso:5912:ed-5:v1:en
Edges and Corners: Must be free of sharp angles/edges to prevent injury during setup, adhering to safety standards.
Tubular Components, Holes and Slots: Accessible openings exceeding 10mm depth (using 7mm or 12mm probes) must be covered to prevent injury.
Shear and Squeeze Points: Acceptable during setup/takedown if controllable and edges are smooth. Mechanical devices should not create accessible shear/squeeze points. Automatic locking devices prevent shear/squeeze points during normal use.
Zippers: Slider, teeth, and tape should be contrasting colors (unless the pull tab is distinct). Door zippers need double sliders. Zippers must meet flat-pull strength requirements.
Guy Rope Systems: Each guy rope combination must withstand minimum tensile force per Table 4, tested by applying force along the ground fastener direction for 1 minute.
Tent and Tent Pole Bags: The tent bag material should meet outer tent fabric standards (Table 2) for protection. Separate bags are needed for poles and pegs to prevent damage/loss.
Inspection Test Methods
Tensile Force of Guy Rope System
To test the tensile force of the guy rope system, first, set up the tent in strict accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. Make sure to close all the doors and windows of the tent to simulate normal use conditions. Then, carefully select and remove one guy rope. For different types of tents, such as A class tents or B class tents, apply the corresponding tensile force to the guy rope system along the direction of the ground fastener. According to the standard, this tensile force should be maintained for 1 minute. During this 1 minute period, observe the performance of the guy rope system, including whether the rope stretches excessively, if the connectors loosen, or if there are any signs of breakage. This test helps to ensure that the guy rope system can effectively withstand the forces exerted on it during actual use, such as those caused by wind or uneven ground, and keep the tent stable.
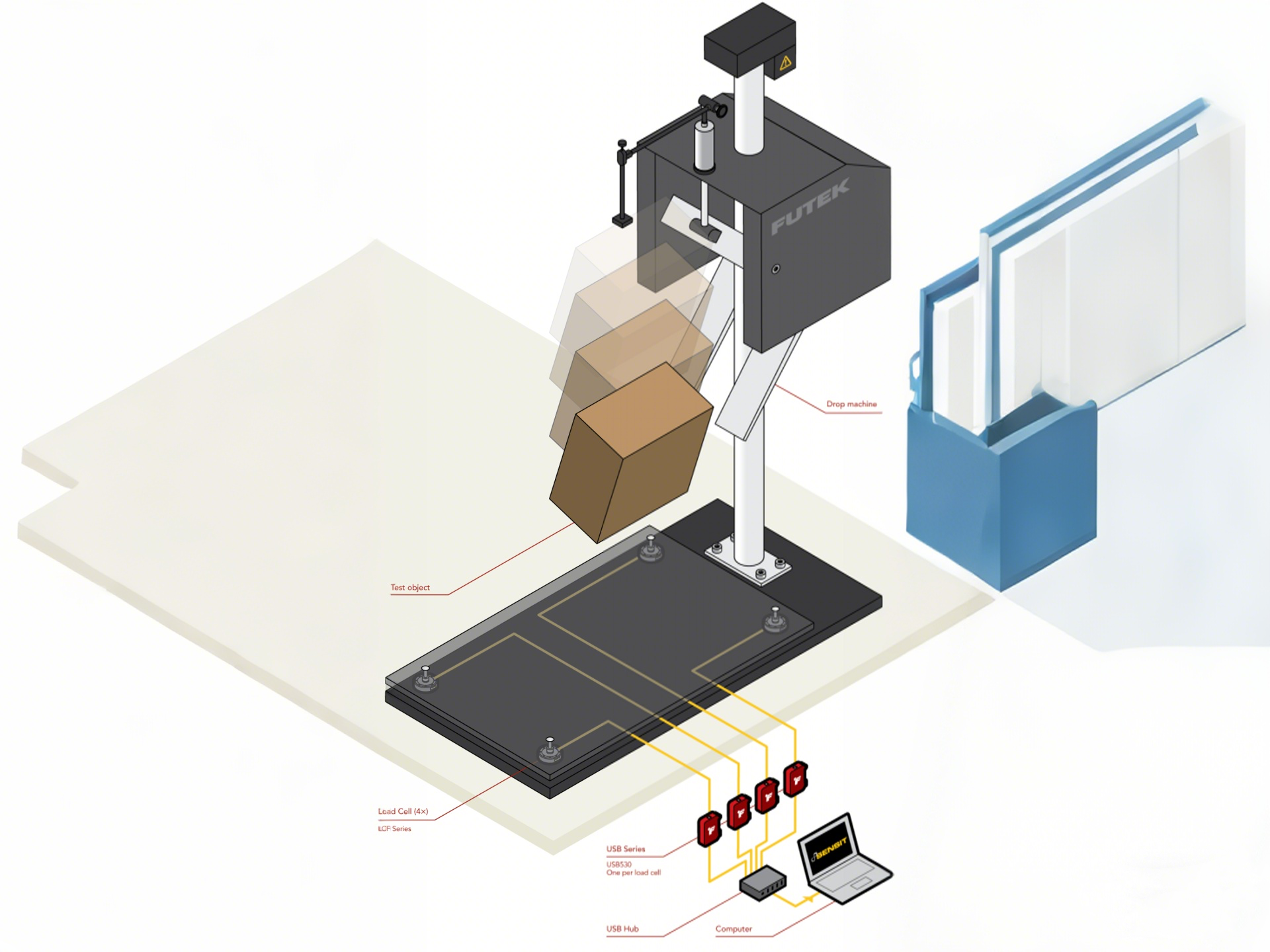
Drop Test
The drop test is carried out with reference to the ISTA 1A standard. First, select a representative sample of the tent and its packaging. The tent should be packed in the same way as it would be for shipping. Then, according to the weight of the package, determine the appropriate drop height from the ISTA 1A standard's weight-height correspondence table. For example, if the package weighs less than 10 kg, the drop height is usually 762 mm. Drop the package from the determined height onto a hard and flat surface, such as a concrete floor. Repeat this process 10 times, each time dropping the package from a different angle to simulate various possible impacts during transportation. After the 10-time drop test, carefully inspect the packaging and the tent inside. There should be no fatal or serious defects. Fatal defects could include major structural damage to the tent, such as a broken tent pole or a torn-open fabric that renders the tent unusable. Serious defects may include significant dents in the packaging that could potentially damage the tent or parts of the tent becoming loose or detached.
Download or view the document about the ISTA 1A standard: http://www.epac-china.com/upload/reference/ISTA-Procedure-1A.pdf
Product Size/Weight Measurement
When measuring the product size, use appropriate measuring tools such as a tape measure for linear dimensions and a caliper for more precise measurements of small components. For example, measure the length, width, and height of the tent when it is fully set up. Compare these measured values with the specifications provided by the manufacturer or with a reference sample. If no specific tolerance is mentioned, a tolerance of +/- 3% is commonly used. For instance, if the specified length of the tent is 2 meters, the acceptable measured length range would be from 1.94 meters to 2.06 meters.
To measure the weight, use a calibrated weighing scale. Place the tent, including all its components such as poles, pegs, and guy ropes, on the scale. The measured weight should also fall within the +/- 3% tolerance range of the specified weight. This ensures that the tent meets the size and weight requirements for practical use and transportation and also helps to maintain consistency in production.

Barcode Scanning Check
The barcode on the tent is an important identifier for inventory management, sales, and product tracking. Use a standard barcode scanner, which can be a handheld device or a scanner integrated into a point-of-sale system. Point the scanner at the barcode on the tent's packaging or on the tent itself if it is directly labeled. The scanner should be able to quickly and accurately read the barcode. After scanning, check that the information displayed on the scanner or the connected system matches the correct product information. This includes details such as the product model number, batch number, and other relevant identification data. If the barcode cannot be scanned or if the scanned information is incorrect, it could lead to issues in supply chain management, incorrect product identification, and potential problems during sales.
For more information on barcode scanning technology and its application in product inspection, you can visit Mechanism of barcode scanning|Technical Information of automatic identification|DENSO WAVE.
Special Function Check
The tent must be able to perform all the functions it claims to have. First, test the installation process. Follow the provided instructions to set up the tent and note any difficulties or issues. For example, if the tent is advertised as having a quick-setup feature, it should be possible to set it up within the claimed time frame without excessive effort or the need for additional tools not provided.
Next, check the adjustment functions. This could include adjusting the height of the tent poles, the tension of the guy ropes, or the position of the tent's internal partitions. Make sure these adjustments are smooth and can be easily locked into place.
Test the switch functions, such as the zippers on the doors and windows. They should open and close smoothly without getting stuck or jamming. For tents with additional features like built-in lighting, test the setting and operation of the lighting system. Check if the lights can be turned on, off, and adjusted in brightness as claimed.
If the tent has a display (such as a digital thermometer or humidity gauge), verify that the display shows accurate and readable information. Finally, test the tent in an actual-use scenario as much as possible. For example, if it is a four-season tent, test its performance in different weather conditions (within the limits of safety) to ensure it can provide the necessary protection and comfort.
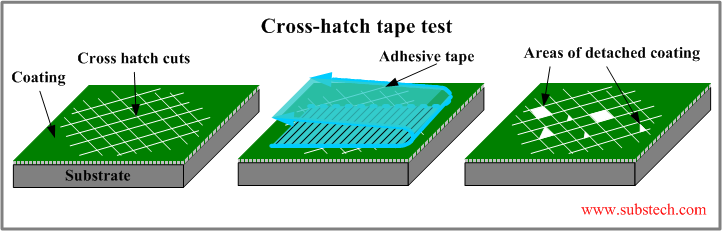
Coating Test
For the coating test, obtain 3M 600 or a similar quality adhesive tape. Select areas on the tent where there is paint, a stamp, a coating, or printing, such as on the outer fabric with a brand logo printed on it or on parts with a protective coating. Press the tape firmly onto the selected area, making sure there are no air bubbles between the tape and the surface. Then, quickly and evenly peel the tape off at a 180 degree angle. Examine the area where the tape was removed. The area of the coating or print that has been pulled off by the tape should not exceed 10% of the total area of the test site. If the percentage of the shedding area is higher, it indicates that the adhesion of the coating or print is insufficient, which may lead to issues such as fading, peeling, or reduced protection over time.
Assembly Test
Begin by carefully reading the tent's assembly instructions. These instructions should be clear, with step-by-step illustrations if possible. Follow the instructions precisely to assemble the tent. As you assemble, check that all the necessary components are present in the package. This includes tent poles, connectors, pegs, guy ropes, and any other parts mentioned in the instructions.
During the assembly process, note if the steps are logical and easy to follow. If there are any parts that are difficult to fit together, or if the instructions seem unclear at any point, it could be a sign of a design or manufacturing issue. Once the tent is fully assembled, inspect the overall finished product. The tent should have a stable and proper shape, with all components fitting together snugly. Check for any loose parts, misaligned poles, or other visible defects. A well-assembled tent should be able to stand on its own without wobbling or collapsing under normal conditions.
Waterproof Check
To perform the waterproof check, set up the tent in a suitable testing area where water runoff can be managed, such as an outdoor area with a sloped surface or a large indoor space with a drainage system. Place the tent with the waterproof side facing up. Use a water-spraying device, such as a garden hose with a spray nozzle adjusted to a moderate spray pattern. Start spraying water onto the waterproof surface of the tent. The water should be sprayed continuously for 2 hours. During this 2-hour period, closely observe the inside of the tent. There should be no signs of wetness or water penetration. After the 2-hour spraying is complete, continue to monitor the inside of the tent for a short period to ensure that no water seeps through later due to water absorption by the fabric. If any water is detected inside the tent, it means the tent fails the waterproof test, and there may be issues with the fabric's waterproof coating, seams, or other components that are supposed to prevent water from entering.
Read a comprehensive guide to IP67 waterproof testing: IP67 Waterproof Testing: What You Need To Know l Leak Testing
The Role of Testcoo in Camping Tent Inspection
When it comes to camping tent inspections, our expertise shines. Our inspectors are familiar with all the requirements and methods detailed in this article, from fabric-related checks to component inspections and test methods. We understand the importance of a high - quality camping tent for outdoor enthusiasts, and we are committed to ensuring that every tent that passes our inspection meets the highest standards of safety, durability, and functionality.
If you are in the market for camping tent inspections or any other product inspection services, look no further than Testcoo. We are here to help you ensure the quality of your products, protect your brand reputation, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Contact us today to discuss your inspection needs.
Free Sample Report Performance Quality Control
Download a sample report to keep control of your supply chain!
Featured Articles
 AQL Table | How to Read It
AQL Table | How to Read It TOP 10 Common Defects in Garments Quality Inspection
TOP 10 Common Defects in Garments Quality Inspection Product Packaging and Shipment Label requirements for Amazon FBA
Product Packaging and Shipment Label requirements for Amazon FBA What Is ASTM-F2413-18? Protective Footwear Standard
What Is ASTM-F2413-18? Protective Footwear Standard How to Conduct Third-Party Quality Control Inspections for Electric Scooters
How to Conduct Third-Party Quality Control Inspections for Electric Scooters SMETA Audit-What is SMETA Audit?
SMETA Audit-What is SMETA Audit? TESTCOO Supplier Verification/Certification Service SLCP, Higg FEM, GRS, GOTS
TESTCOO Supplier Verification/Certification Service SLCP, Higg FEM, GRS, GOTS Quality Control Inspection Company in China
Quality Control Inspection Company in China What is Quality Inspection? A Complete Guide
What is Quality Inspection? A Complete Guide Guidelines for Product Inspection in India
Guidelines for Product Inspection in India
Category
- Production Inspection Service
- Factory Audit
- Softline Inspection
- Hardline Inspection
- Electrics Inspection
- Certification
- Checklist
- Manufacturers
- Quality Assurance Basics
- Products Recall
- AQL
- Guidence and Standard
- News
- Supplier Management
- Amazon
- Protective Equipment
- e-commerce quality control
- Indian Manufacturing
- Soft Goods Quality Control
- Supply Chain Management
- Supply Chain Resilience
- E-Commerce Quality Control
- ISO 2859
- Supply Chain Optimization
- Garment Industry
- Higg Index




