Quality Assurance vs. Quality Control: 5 Key Differences Explained

In modern quality management, two essential processes Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) are crucial in ensuring the highest standards of product quality. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct activities with different roles in quality management. Both are essential components of a quality system, especially in regulated industries like life sciences, where adherence to standards such as FDA 21 CFR 820 or ISO 9001 is mandatory.
This article explains the differences between Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC), providing a clearer understanding of each concept and how they contribute to overall product quality.
What is Quality Assurance?
Quality Assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of any quality management system (QMS) and is widely implemented across regulated sectors, including life sciences. In essence, QA refers to the proactive measures and systems that are put in place to ensure that products or services consistently meet defined quality standards.
Breaking Down Quality Assurance
Quality assurance involves more than just meeting basic compliance requirements. To be effective, QA requires creating a formalized system of policies, procedures, and plans designed to ensure products are manufactured according to regulatory and internal standards. For instance, a manufacturer regulated by the FDA would need to adhere to current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) requirements, which dictate the framework for ensuring product quality throughout production.
A well-implemented QA system doesn’t just aim for regulatory compliance but also strives to improve the overall quality of the product. Companies often set internal quality benchmarks (such as acceptable defect percentages) to further enhance customer satisfaction and product safety.
In short, quality assurance is the practice of putting in place systematic measures to "assure" that products meet quality expectations and compliance standards.
Further Read about the difference between QA and compliance: https://www.testcoo.com/en/blog/quality-assurance-vs-compliance
What Does QA Mean in Practice?
The acronym "QA" stands for Quality Assurance. In the context of your business, implementing QA means creating repeatable, measurable processes within your operations designed to prevent errors, defects, or deviations from occurring in the first place. QA focuses on proactively establishing processes that ensure consistent product quality rather than merely identifying and fixing problems after they happen.
Effective quality assurance means defining clear quality standards, implementing processes to meet those standards, and continually evaluating and refining the results. One well-known quality assurance framework is ISO 9001:2015, the globally recognized standard for quality management systems. ISO 9001 sets a clear roadmap for how organizations should establish and maintain their quality assurance processes, and it serves as the foundation for more industry-specific standards, such as ISO 13485 for medical devices.
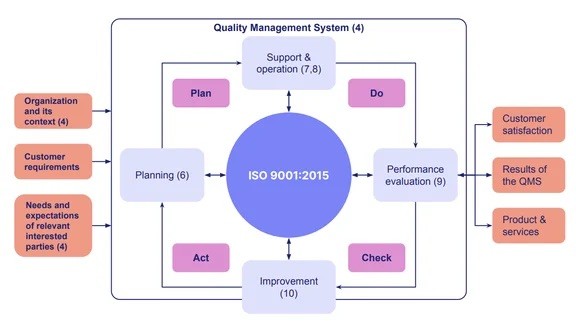
What is Quality Control?
While QA is focused on preventing issues, Quality Control (QC) is more about identifying and addressing problems after they’ve occurred. QC refers to the processes involved in inspecting, testing, and measuring products to ensure they meet the required quality standards.
While QA is preventive, QC is corrective. It involves the actual inspection and testing of products to ensure they conform to quality specifications. QC is typically performed at different stages throughout the production process, where specific quality attributes of a product are measured, and non-conformities are identified.
Key Differences Between Quality Assurance and Quality Control
Despite both being essential elements of a quality management system, QA and QC serve different purposes. Here are five key differences between the two:
1. Focus:
- Quality Assurance (QA) is focused on building and improving processes to prevent defects.
- Quality Control (QC) is concerned with identifying and fixing defects in the final product.
2. Approach:
- QA involves systematic planning and process management to ensure quality standards are met during production.
- QC relies on inspections, tests, and measurements to detect defects after production.
3. Timing:
- QA is a proactive approach that is implemented throughout the product lifecycle.
- QC is reactive, focusing on catching defects during or after production.
4. Scope:
- QA addresses the entire process and aims to prevent issues from arising in the first place.
- QC is more focused on the end product and ensuring it meets quality requirements.
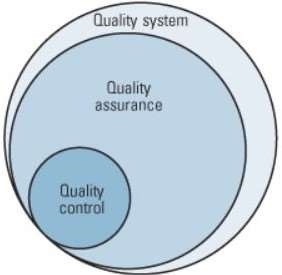
5. End Goal:
- The goal of QA is to create processes that deliver consistent, high-quality products.
- The goal of QC is to identify defects and ensure that only products that meet the required standards reach customers.
Total Quality Management (TQM) and QA
A holistic approach to quality management, known as Total Quality Management (TQM), emphasizes the involvement of all employees in improving processes, products, and services. TQM is a customer-centric methodology where everyone in the organization is empowered to make improvements, ensuring the final product consistently meets customer expectations.
TQM, along with frameworks like ISO 9001, focuses on creating an organizational culture where continuous improvement is a shared responsibility, helping companies meet quality standards and maximize customer satisfaction.
In summary, while Quality Assurance (QA) focuses on proactive planning and process management to ensure quality throughout the production cycle, Quality Control (QC) involves reactive testing and inspections to identify and fix defects in the final product. Both processes are vital, but they function at different stages and serve complementary roles in maintaining product quality.
Free Sample Report Performance Quality Control
Download a sample report to keep control of your supply chain!
Featured Articles
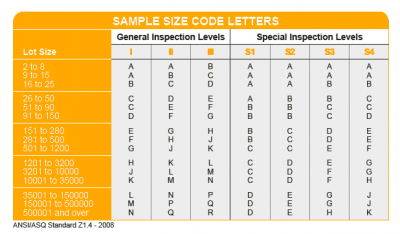 AQL Table | How to Read It
AQL Table | How to Read It TOP 10 Common Defects in Garments Quality Inspection
TOP 10 Common Defects in Garments Quality Inspection Product Packaging and Shipment Label requirements for Amazon FBA
Product Packaging and Shipment Label requirements for Amazon FBA What Is ASTM-F2413-18? Protective Footwear Standard
What Is ASTM-F2413-18? Protective Footwear Standard How to Conduct Third-Party Quality Control Inspections for Electric Scooters
How to Conduct Third-Party Quality Control Inspections for Electric Scooters SMETA Audit-What is SMETA Audit?
SMETA Audit-What is SMETA Audit? TESTCOO Supplier Verification/Certification Service SLCP, Higg FEM, GRS, GOTS
TESTCOO Supplier Verification/Certification Service SLCP, Higg FEM, GRS, GOTS Quality Control Inspection Company in China
Quality Control Inspection Company in China What is Quality Inspection? A Complete Guide
What is Quality Inspection? A Complete Guide Guidelines for Product Inspection in India
Guidelines for Product Inspection in India
Category
- Production Inspection Service
- Factory Audit
- Softline Inspection
- Hardline Inspection
- Electrics Inspection
- Certification
- Checklist
- Manufacturers
- Quality Assurance Basics
- Products Recall
- AQL
- Guidence and Standard
- News
- Supplier Management
- Amazon
- Protective Equipment
- e-commerce quality control
- Indian Manufacturing
- Soft Goods Quality Control
- Supply Chain Management
- Supply Chain Resilience
- E-Commerce Quality Control
- ISO 2859
- Supply Chain Optimization
- Garment Industry
- Higg Index




