Understanding C-TPAT: The Key to Secure Trade with the U.S.

↵
In international trade, particularly with the United States, the Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism (C-TPAT) plays a crucial role in securing global supply chains. But what exactly is C-TPAT, and why is it important? In this blog, we’ll break down C-TPAT standards, the audit process, and the key benefits of certification for businesses involved in cross-border trade.
What is C-TPAT?
Full Name: Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism (C-TPAT)
Developed By: Customs and Border Protection (CBP) under The US Department of Homeland Security
Why Was C-TPAT Established?
After the 9/11 attacks, CBP aimed to collaborate with related industries to establish a supply chain security management system. The goal is to ensure the safety of transportation, secure information flow, and cargo conditions from origin to destination, ultimately preventing terrorism.
Implementation Date: April 16, 2002.
Who Needs C-TPAT Certification?
C-TPAT applies to various industry players, including:
- US importers
- Air, Ocean and Rail carriers
- Freight consolidators
- Non-vessel operating common carriers
- US port authorities and Terminal operators
- Foreign manufacturers and Warehouse operators
Discover the various types of audits happening in the manufacturing industry here.
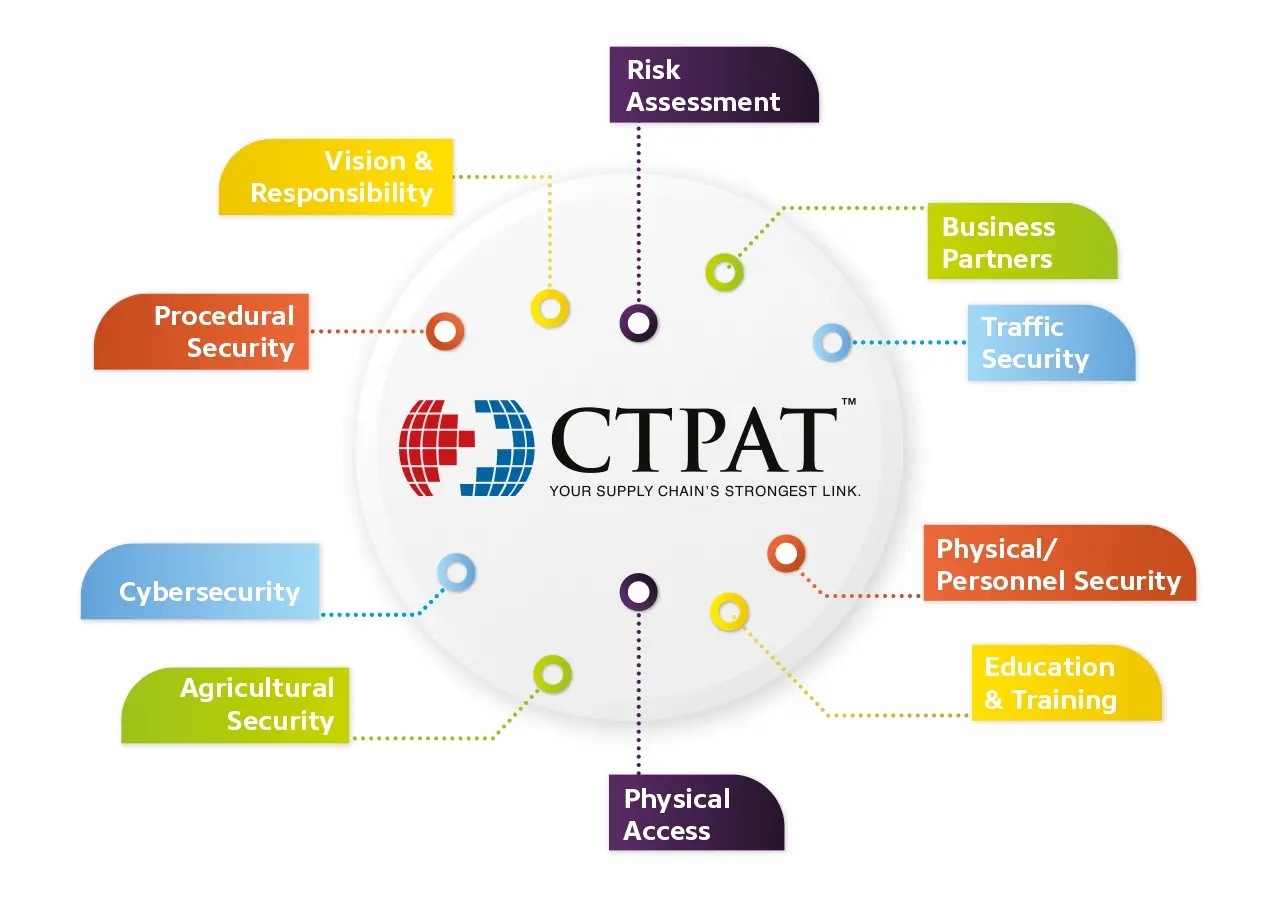
C-TPAT Compliance: Key Security Requirements
To qualify for C-TPAT certification, foreign manufacturers must meet specific minimum security criteria, including:
Corporate Security
- Security Vision and Responsibility
- Risk Management
- Business Partners
- Cybersecurity
Transportation Security
- Conveyance and Instruments of International Traffic Security
- Seal Security
- Procedural Security
- Agriculture Security
Personnel and Physical Security
- Physical Security
- Physical Access Control
- Personnel Security
- Security Training and Threat Awareness
For an in-depth list, check the official CBP guidelines here.
How to Check C-TPAT Certification Status?
C-TPAT participants can verify certification status through CBP’s Status Verification Interface (SVI):
- SVI (Status Verification Interface): A web portal created by CBP for C-TPAT applicants to verify certification status and type.
- SVI (Status Verification Interface Participant): A participant in the SVI system can use the CBP website to check another SVIP's certification status.
- SVIP ID: Each SVIP has at least one ID number that can be provided to customers via the CBP website to confirm C-TPAT status.
CBP offers an official website for C-TPAT certification status verification.
Quicky check the certification status here.
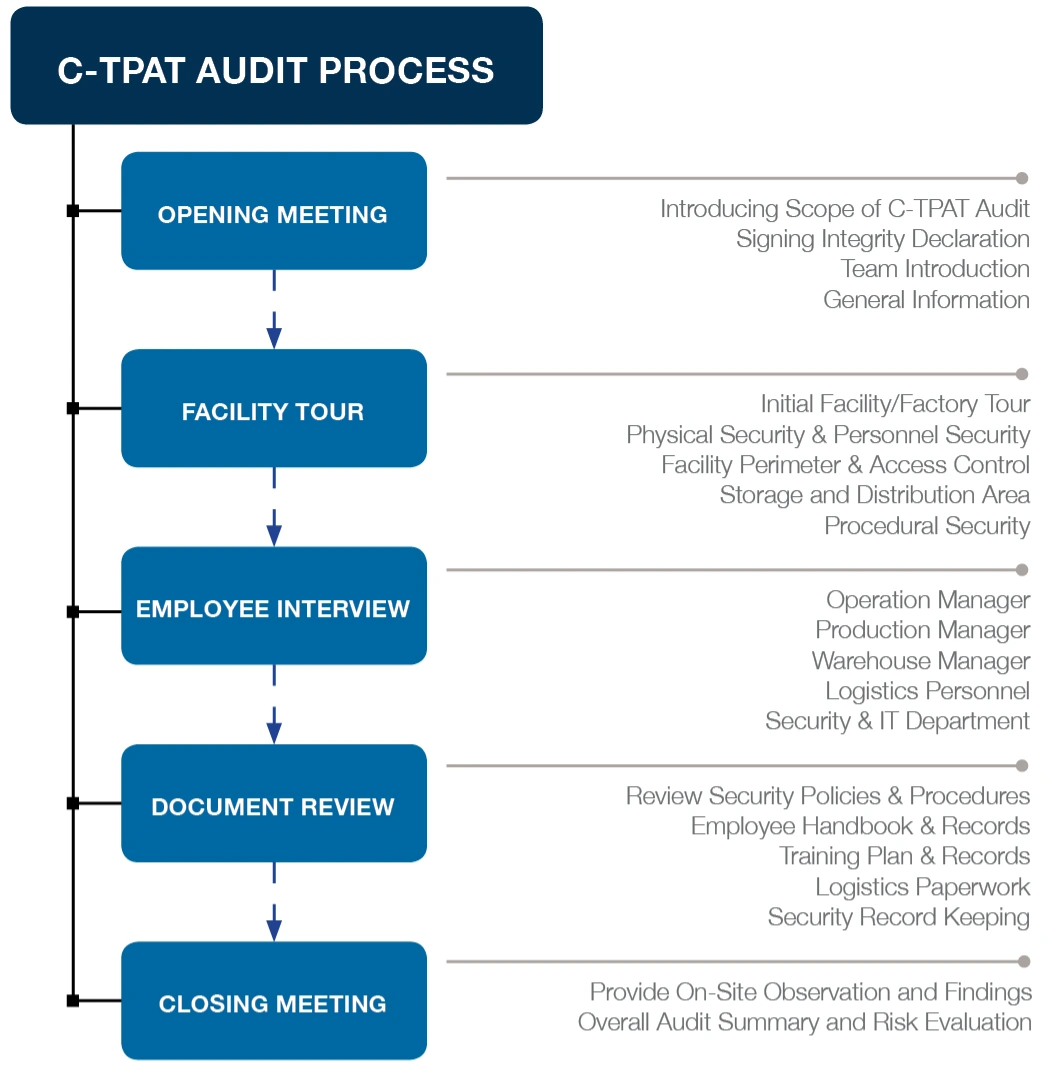
C-TPAT Audit Process: Step-by-Step Guide
A C-TPAT audit involves a comprehensive evaluation of a company’s supply chain security measures. Here’s what to expect:
- Opening Meeting
- Introduce the audit scope
- Execute the audit
- Assign representatives to accompany auditors
- Adjust formats
- Facility Tour
- Confirm audit deficiencies
- Summarize reports
- Weekly safety measures
- Input and output delivery points
- External lighting systems
- Vehicle parking areas
- Container storage
- Access control
- Security equipment
- Employee Interviews
- Security procedures and management regulations
- Anti-terrorism security guidelines and manuals
- HR managers
- Production managers
- Warehouse managers
- Shipping managers
- Security managers
- Logistics managers
- IT leads
- Document Review
- Security procedures and management policies
- Employee security guidelines and manuals
- Employee files
- Security training plans and records
- Shipping documents
- Loading/unloading records
- Container handling areas
- Security patrol logs
- Other relevant records
- Closing Meeting
- Provide a verbal summary of on-site findings
- Summarize overall observations
↵ ↵
Meeting C-TPAT’s Five-Step Risk Assessment
C-TPAT has established the Five-Step Risk Assessment Guide to help members conduct comprehensive risk assessments to effectively manage risks within the supply chain. The guide can be found on the CBP website.
Steps:
- Map Cargo Flow and Identify Business Partners
Trace the movement of goods across the supply chain, including transportation methods (air, sea, rail, truck) and key nodes (country of origin, transit points).
- Conduct Threat Assessment
List potential threats in countries involved, such as terrorism, human and contraband trafficking, agricultural/public health threats, and organized crime, and rank these threats.
- Perform Vulnerability Assessment
Identify potential targets for terrorists or criminals within partner operations, such as data or access to goods and information. Address weaknesses in company procedures to prevent access to these assets.
- Develop an Action Plan
Document weaknesses, assign responsibility, set deadlines, and report results to management. Follow up on changes made to address the identified risks.
- Document Risk Assessment Process
Regularly review and update the procedures, with at least an annual review. High-risk supply chains and road transport companies should perform more frequent evaluations.
For the official C-TPAT risk assessment guide, visit CBP's website
Guidelines for Vendors Applying for C-TPAT
When preparing to meet the five-step risk assessment process, vendors should include the following:
- Date of creation and most recent revision of the risk assessment process.
- Identify personnel responsible for maintaining the process, including alternates.
- Specify the frequency of risk assessments (e.g., annually, quarterly, or whenever new supply chain partners are added).
- Outline the frequency of reviewing and updating actual risk assessment procedures.
- Methods for conducting threat assessments on international supply chains.
- Methods for conducting vulnerability assessments (e.g., verifying C-TPAT/PIP/AEO status, on-site visits by quality assurance managers, security analysis questionnaires).
- Procedures for addressing vulnerabilities (e.g., on-site visits or contract termination).
- Training for key personnel involved in the risk assessment process.
- Internal oversight and assignment of responsibilities to ensure consistent and effective implementation of the process.
Benefits from C-TPAT
C-TPAT is mostly required by American brands. Although it is not a mandatory requirement, suppliers have the following benefits after passing the anti-terrorism factory audit certification:
- Reduced CBP examinations - Companies that participate in C-TPAT may experience fewer inspections by the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP).
- Shorter wait times - Companies that participate in C-TPAT may experience shorter wait times at the border.
- Front of the line inspections - Companies that participate in C-TPAT may be able to receive front of the line inspections.
- Access to FAST Lanes - Companies that participate in C-TPAT may have access to the Free and Secure Trade (FAST) Lanes at land borders.
- Supply Chain Security Specialist - Companies that participate in C-TPAT may be assigned a Supply Chain Security Specialist.
- Importer Self-Assessment Program (ISA) eligibility - Importers that participate in C-TPAT may be eligible to participate in the Importer Self-Assessment Program (ISA).
- Security technology - Companies that participate in C-TPAT may have access to security technology to strengthen physical security requirements.
- Agricultural security - Companies that participate in C-TPAT may be required to put in place measures to prevent unauthorized chemicals or biological agents from entering the supply chain.
- Physical security - Companies that participate in CTPAT may be required to control access to sensitive areas like cargo, equipment, and facilities.
- Streamlined cargo flow - Companies that participate in CTPAT may help streamline cargo flowing in and out of the United States.
How Testcoo Can Help with C-TPAT Audits
Navigating C-TPAT compliance can be complex, but Testcoo’s expert auditors make the process seamless. Our global audit network ensures:
- On-site inspections within 48 hours
- Comprehensive reports covering security gaps
- Guidance on corrective actions & compliance improvements
Quickly browse our all audit service types and create your plan.
Easily schedule your C-TPAT audit through our website or contact us to find out more!
Free Sample Report Performance Quality Control
Download a sample report to keep control of your supply chain!
Featured Articles
 AQL Table | How to Read It
AQL Table | How to Read It TOP 10 Common Defects in Garments Quality Inspection
TOP 10 Common Defects in Garments Quality Inspection Product Packaging and Shipment Label requirements for Amazon FBA
Product Packaging and Shipment Label requirements for Amazon FBA What Is ASTM-F2413-18? Protective Footwear Standard
What Is ASTM-F2413-18? Protective Footwear Standard How to Conduct Third-Party Quality Control Inspections for Electric Scooters
How to Conduct Third-Party Quality Control Inspections for Electric Scooters SMETA Audit-What is SMETA Audit?
SMETA Audit-What is SMETA Audit? TESTCOO Supplier Verification/Certification Service SLCP, Higg FEM, GRS, GOTS
TESTCOO Supplier Verification/Certification Service SLCP, Higg FEM, GRS, GOTS Quality Control Inspection Company in China
Quality Control Inspection Company in China What is Quality Inspection? A Complete Guide
What is Quality Inspection? A Complete Guide Guidelines for Product Inspection in India
Guidelines for Product Inspection in India
Category
- Production Inspection Service
- Factory Audit
- Softline Inspection
- Hardline Inspection
- Electrics Inspection
- Certification
- Checklist
- Manufacturers
- Quality Assurance Basics
- Products Recall
- AQL
- Guidence and Standard
- News
- Supplier Management
- Amazon
- Protective Equipment
- e-commerce quality control
- Indian Manufacturing
- Soft Goods Quality Control
- Supply Chain Management
- Supply Chain Resilience
- E-Commerce Quality Control
- ISO 2859
- Supply Chain Optimization
- Garment Industry
- Higg Index

